|
Figure 1�@
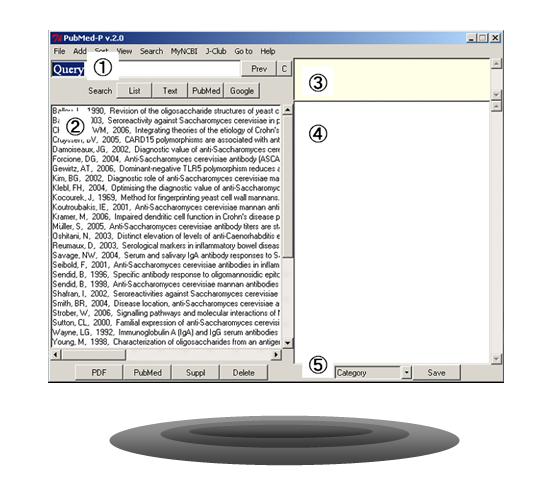
|
|
Management of PDF files
Setting up�F
Expand downloaded pubmed_beta.zip and save the pubmed folder with its
contents anywhere you want.
However, if you are using a language other than English in your OS,
save the folder directly below C:\ directory.
Note: This program was tested under Windows XP and 7 but not
Windows Vista.
Registration of your PDF files�F
Start PubMed-P by double clicking pubmed-P.exe. PubMed-P window (Fig. 1) will show up.
I. Registration of multiple PDF files (batch)
Place your PDF files in the pubmed folder and select �gAdd pdf files (batch)�h
from �gAdd�h menu. A sub-window
will show up, so click �gStart�h button.
Please wait until the sub-window automatically closes. More than half of recent publications
will be registered automatically by executing this function. The ones PubMed-P failed to register
will remain in the pubmed folder (rest will be in �gcnvd�h folder). You can easily (semi-automatically)
register the remaining files using the following function.
II. Registration of a single file
Drag & Drop your file on to the list box �A (Fig. 1)
1) If
your file is named PMID.pdf, it will be registered automatically.
2) Files
with any name (other than a sequence of numbers*) may also be registered
automatically.
*
PubMed-P recognize any sequence of number as PMID if it is used in a file name, so change the
file name if it is not your intension.
3) If
PubMed-P was unable to register your file, a sub-window will pop-up. Text
extracted from your file
may show
up in the lower-left text box.
( Semi-automatic registration using the subwindow )
�E�@Input keywords that
would identify the publication to the upper left text box (horizontal).
(You can copy keywords from the text on the
sub-window or from PDF file and then paste .
Also, double clicking words in the extracted text will insert the word
into the text box�j
�E�@Press �gSearch�h
button and search result will show up in the right list box.
�E�@Click on the
corresponding publication and press �gSelect�h button.
# PubMed-P will ask you if you want the PDF to be moved to �gcnvd�h or �gpmid�h
folder. If you do, close PDF file if open and the click OK button.
# PubMed-P retrieves information from PubMed via internet. You may need to set Proxy information
(port, ID, and/or pass).
Main functions�F
Double-click on a publication in the list �A(Fig. 1) to open the PDF file.
Information (authors, title, abstract, your comment, category) will appear on
the PubMed-P window when you click on a paper in the list �A(Fig. 1). With a paper being selected, you
can access PDF file, PubMed, and Suppl (supplemental files) by pressing the
corresponding button (below the list �A).
You can add your comments to the upper-right text box �B (Fig. 1). Also, supplemental files on your local
computer can be associated with a paper by Drag & Drap-ing a file to the
text box �B (Fig. 1). A paper in the list box �A should be selected to use these functions.
You can set a category name using the lower-right pull-down menu �D (Fig. 1). Category name you entered will be
saved in the menu, so you do not need to repeat typing same thing. Important: When you make any changes to comment
and category, click �gSave�h button.
When Pubmed-P is restarted after adding category, the category name will show
up under �gView�h menu, so you can see the list of papers in the category by
selecting it.
The list �A can be sorted (descending or ascending order) by author or year using Sort/Author,
Year function (menu).
Type your query in the entry box �@ and hit �gList�h button to find a paper you
need. Author, title, abstract and
comment are the target of the search.
Buttons and Menus:
I. Buttons
Search�@keywords
typed in the text box �@ (Fig. 1)
Prev: Shows previous keywords you typed in
the text box.
List: Information
in the list of your papers (author, title, abstract and comment).
Text: Text files
in the pubmed/text folder
PubMed: PubMed.. of course�c
Google: Google Scholar
Lower-left buttons will show the information of the
selected paper �c
by opening
�gPDF�h file,
by opening
�gPubMed�h using your
default browser,
by opening
�gSuppl�h files, OR
�gDelete�h the information from your list. (PDF file will be moved to
pubmed/trash folder)
II. Menus
File/Open pmid folder: You
know what I mean�c
/Export to EndNote:
Information of papers shown
in the list on PubMed-P will be converted to MedLine format so that you can
import using
EndNote. The formatted infomation
will be saved in pubmed/medline.txt.
Open EndNote and then
select menu, File/Import. Choose the medline.txt in the box next
to
�gChoose file�h, change Import option to PubMed(NLM), and click Import
button.
/Check files: See if
there are un-registered PDF files in pmid folder.
/Exit : You know what I mean�c
Add/Add pdf files (batch):
Explained above in the
section of main functions.
/Add suppl. data:
Select a paper in the list
box �A and then use this
function to relate any files on your local computer.
Sort/Author (a-z,z-a) : Sort the list �A by names of first authors
/Year (new,old) : Sort the list �A by Year of
publication
View/All...: Select a categry to display on the list �A
Search/List : Author names, title, abstract and comment
will be searched by keyword(s) in text box �@
/Text :
See below �gFull Text Search�h section
/PubMed : You know what I mean�c
/G-Scholar : You know what I mean�c
MyNCBI/Search :
For example if you type
"interleukin" and select this function, you can see papers on
interleukin
published in the past one week.
When you search the same key word, papers published between
the date and the
latest search date will be searched.
J-Club/Style1, Style2: See below �gMaking a list of papers selected on
PubMed�h section
Help/Readme : Open README.txt or help2.html file
|
|
Full text
search:
|
|
Any text files in "text" folder can be
searched with your query. Save your PDF files in text format before using
this function.
If you are using Acrobat Reader, select text information by using "Menu
bar: Edit/Select All" function and copy-paste on a text editor (ex.
Notepad). If you have Adobe Acrobat, use "Menu bar: File/Save as (Text,
Accessible)" function. All the text files need to be saved in
C:/pubmed/text folder. It would be convenient if you just keep file names as
"PMID.txt"
.
Type your query in the text box of PubMed-P and select "Menu bar:
Search/Text (w)" function. Search result will appear on an IE window
(see Example 1).
If your query was found in PMID.txt files,
links to PubMed, your file lists and PDF (with Search links�jwill be added to the search result.
If you are familliar with Regular Expression, more sophisticated search is
possible. In this case, use "Menu bar: Search/Text(s)" function.
For example, if you enter "statistical
analysis(.{1,1000}?)results", description of statistical analysis will
be nicely picked up (see Example 2)
|
|
�iExample 1�j
16449960.txt Chamberlin, WM.,
Naser, SA., , Integrating
theories of the etiology of Crohn's Disease On the etiology of Crohn's
Disease: Questioning the Hypotheses. PubMed | List |
PDF
<1>... in infl ammation�h[7]. This hypothesis is challenged by the
Ferwerda et al. who show that wild-type NOD2 and Toll-Like Receptors (TLR-2
and TLR-4) are non-redundant recognition systems that act synergistically
in response to mycobacterial antigens [8]. Sechi found that over 70% of CD
patients with a NOD2 mutation had PCR evidence of a MAP infection. This fi ndings suggests that a
specific pathogen may b ...
�iExample 2�j
12195191.txt Kim, BG., Kim,
YS., Kim, JS., Jung, HC., Song, IS., , Diagnostic
role of anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae mannan antibodies combined with
antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in patients with inflammatory bowel
disease. PubMed | List |
PDF
> Statistical Analysis. We used a chi-squared test or Fisher�fs exact test
for categorical variables. For continuous variables, a two-sample t-test or
Wilcoxon�fs rank-sum test was used. A P value less than 0.05 was considered
statistically significant. SPSS 10.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) was used for both data management and statistical
analysis.
|
|
Making a
list of papers selected on PubMed:
|
|
On PubMed
website, select papers you want to save and change display format to XML
(Fig. 2, 1). Select "File" from "Send to" pull-down menu
(Fig. 2, 2) and save "pubmed-result.txt" file in C:/pubmed .
|
|
Figure 2
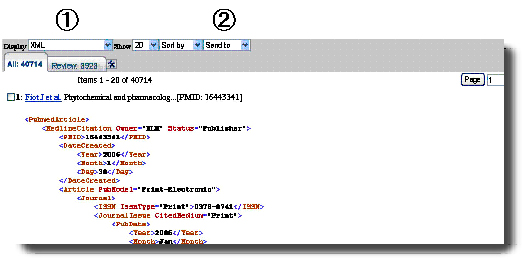
|
|
On PubMed-P window,
select "Menu bar: J-Club/Style1 or Style 2" (Fig. 1). And then, in the
new pop-up window, select HTML file which you want to save the information in
the new window popped up. If you use this function for the first time or want
to create a new HTML file, type a name in the pop-up window and click
"New" button. The list shown below will be automatically created
(Fig. 3). If you choose "Style1 or Style 2 (rvs)", info of papers
will be sorted in ascending (old->new) order.
If you choose an existing HTML file, the information will be appended.
|
|
Figure 3
|
|
Style
1
1. Fiot, J., Sanon, S., Azas, N., Mahiou, V., Jansen, O., Angenot, L.,
Balansard, G., and Ollivier, E. "Phytochemical and pharmacological
study of roots and leaves of Guiera senegalensis J.F. Gmel
(Combretaceae)." J Ethnopharmacol, 2006, In press:
[PubMed]
2. Dev, V., Phookan, S., Sharma, VP., Dash, AP., and Anand, SP.
"Malaria parasite burden and treatment seeking behavior in ethnic
communities of Assam, Northeastern India." J Infect, 2006, 52:
131-9 [PubMed]
Style 2
1. Fiot, J., Sanon, S., Azas, N., et al. (2006) Phytochemical
and pharmacological study of roots and leaves of Guiera senegalensis J.F.
Gmel (Combretaceae). J Ethnopharmacol, In
press: [PubMed]
2. Dev, V., Phookan, S., Sharma, VP., et al. (2006) Malaria
parasite burden and treatment seeking behavior in ethnic communities of Assam, Northeastern India. J Infect, 52:
131-9 [PubMed]
|

